Lecture Materials
Unit III: Protein Function
Lecture 3 - Hemoglobin: A Case Study of Protein Structure-Function Relationships
Hemoglobin (Hb) and Myoglobin (Mb) function as oxygen transport and storage molecules in higher organisms. There functions have been long studied and, together, provide a wealth of examples of how the structure and function of proteins are related.
- Lecture 3 Overheads
- Reading: Berg et al., Chapter 7: Hemoglobin: Portrait of a Protein in Action
- Additional Reading
- Crystal structure of myoglobin
- Kendrew, J.C., Bodo, G., Dintzis, Parrish, R.G. and Wyckoff, H., "A Three-Dimensional Model of the Myoglobin Molecule Obtained by X-Ray Analysis", Nature 1958, 181, 662-666.
- Crystal structure of hemoglobin
- Perutz, Max, "RElation Between Structure and Sequence of Haemoglobin", Nature 1962, 194, 914-917
- Crystal structure of myoglobin
- Models
- Problem Assignments
Lecture 4 - Enzymes: Basic Concepts and Kinetics
Enzymes are biological catalysts. Nearly every reaction that takes place in a living cell is catalyzed by an enzyme. Most enzymes are proteins. Beside their role in speeding up the rates of chemical reactions, enzymes also play an important role in controlling the flow of material through the myriad of metabolic pathways required to sustain a living cell.
- Lecture 4 Overheads Reading: Berg et al., Chapter 8: Enzymes: Basic Concepts
- Models
- Publisher's Living Figure illustrates the active site crevice in lysozyme
- Hexokinase demonstrates concept of induced fit
- Problem Assignments
- Resources
Lecture 5 - Catalytic Strategies
Enzymes have evolved an array of different strategies or enhancing the power and specificity of the reactions they catalyze. For numerous enzymes the details have been worked out at the atomic level. In this lecture we will focus on four examples: chymotrypsin, carbonic anhydrase, the EcoRV restriction endonuclease, and nucleoside monophosphate kinases.
- Lecture 5 Overheads
- Reading: Berg et al., Chapter 9: Catalytic Strategies
- Additional Reading
- Metabolic Reconstruction
- Zhang, Ying et al., "Three-Dimensional Structural View of the Central Metabolic Network of Thermotoga maritima" Science 2009, 325, 1544-154
- Metabolic Reconstruction
- Animations
- Models
- You Tube Video
- Problem Assignments
Lecture 6 - Regulatory Strategies
Living cells contain thousands of metabolites linked to one another by a dizzying array of chemical reactions. These reactions link one metabolite to another and collectively are arranged into metabolic pathways, which crisscross and intersect to form a large interconnected network. Each reaction is catalyzed by one or more enzymes and many of these enzymes play a large role in controlling the flow of material through the network. In this lecture we will focus on some of the strategies used to regulate enzyme activity, and consequently, metabolic processes.
- Lecture 6 Overheads
- Reading: Berg et al., Chapter 10: Regulatory Strategies
- Models
- Resources
- Problem Assignments

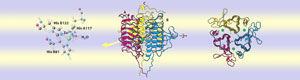
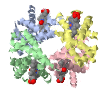
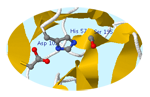 Chymotrypsin exhibits catalytic principles
Chymotrypsin exhibits catalytic principles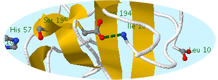 Chymotrypsin example of proteolytic activation
Chymotrypsin example of proteolytic activation