Human Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase
(pdb id 1s80)
Human Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase is an enzyme that has not been
nearly as extensively studied as E. coli Alkaline Phosphatase. However by
combining what we know about the human epoxide hydrolase with what we know about
other epoxide hydrolases from other organisms (bacteria) a considerable amount can be stated.
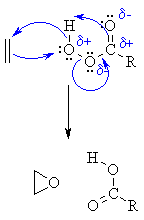
Epoxide hydrolases have the important role of catalyzing the reaction that forms a
glycol (or diol) from an epoxide.
This conversion is an important one because
epoxides are quite chemically reactive and thus can be quite harmful to a cell [5]. Due
to their importance epoxide hydrolases are found in many types of human tissues including kidney,
liver, and vascular types where they act on lipid epoxide substrates.They also play an important role in cell signaling pathways.
One pathway they influence is the regulation of blood pressure. Soluble epoxide hydrolase
catalyzes the hydrolysis of cis-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid which affects the kidneys
, blood vessels, and heart, causing an increase in blood pressure. Another system that the
enzyme influences is the respiratory system. By catalyzing the hydrolysis of leukotoxin and
isoleukotoxin, the corresponding diols of which are implicated in the inflammatory cascade,
epoxide hydrolase also plays a role in acute respiratory distress
syndrome [3].
The folding topology of the above protein as classified by the SCOP database is HAD-like. This fold involves 3 layers like a cheese sandwich. In this case the helices are the bread, and the sheets are the cheese.
Page 2
