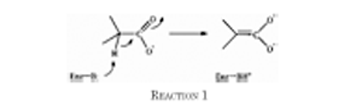
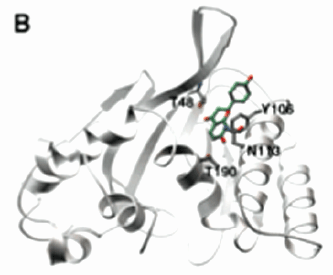
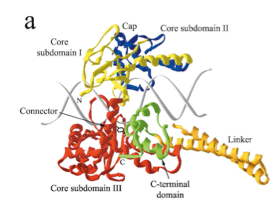
Isomerases are just one of the six categories of enzymes. There are many subcategories of isomerases that fit in the large class. Isomerases conduct a reaction that rearranges particular atoms within the molecule (1). Usually their role is to prepare a molecule for subsequent reactions. Many databases were searched to find examples of three non-homologous isomerases. After doing a sequence alignment, three non-homologous enzymes from different subcategories were chosen. These three examples are chalcone isomerase, mandelate racemase and DNA topoisomerase 1.
The three examples start off differing by the cellular location of each enzyme. Chalcone isomerase is found in plant cells that are involved with flowering (2). In contrast, mandelate racemase is found in Pseudomonas putida, which is a soil bacteria (3). The third example is found in all organisms, but found in different cellular areas. DNA topoisomerase 1 is found in the nucleus of eukaryotes and found in the cytosol of bacteria. All three of these enzymes are not only found in different organisms, but also found in different cellular locations.