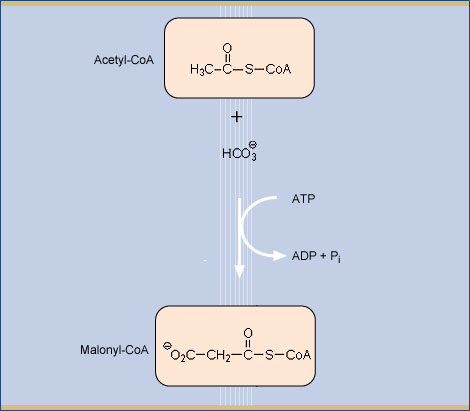
Acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase catalyzes the first committed step of fatty acid biosynthesis. Universally, this reaction involves three functional components all related to a carboxybiotinyl intermediate. A biotinyl domain shuttles its covalently attached biotin prosthetic group between the active sites of a biotin carboxylase and a carboxyl transferase. In Escherichia coli, the three components reside in separate subunits: a biotinyl domain is the functional portion of one of these, biotin carboxy carrier protein (BCCP). The structure of Acetyl Co-A carboxylase may be described as a capped beta sandwich with quasi-dyad symmetry. Each half contains a characteristic hammerhead motif. The biotinylated lysin is located at a hairpin beta turn which connects the two symmetric halves of the molecule, and its biotinyl group interacts with a non-symmetric protrusion from the core. Biotin is stabilized in its binding pocket by Met124, Lys122, Tyr92, and Thr 94. Shown below is a schematic of the biochemical conversion that Acetyl CoA Carboxylase catalyzes.