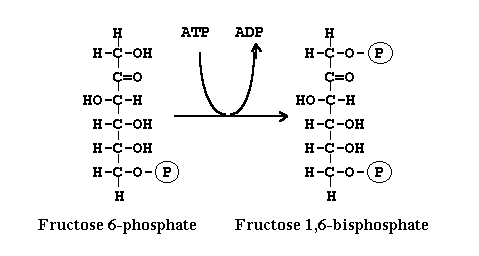
REACTION
MECHANISM FOR THE CONVERSION OF FRUCTOSE 6-PHOSPHATE TO FRUCTOSE 1,6-BISPHOSPHATE

Fructose 6-phosphate is phosphorylated by ATP to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. This reaction is catalyzed by phosphofructokinase, an allosteric enzyme. The reaction rate of glycolysis is critically dependent on the level of activity of this enzyme, which is allosterically controlled by ATP. This allosteric effect is elicited by the binding of ATP to a specific regulatory site that is distinct from the catalytic site. The inhibitory action of ATP is reversed by AMP, and so the the activity of the enzyme increases when the ATP/AMP ratio is lowered. In other words, glycolysis is stimulated as the energy charge falls. (5)
The conversion of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is of the phosphoryl transfer type of reaction. The reaction is irreversible under physiological conditions. Standard state delta G' for the reaction is -3.4 Kcal/mol. Delta G for the reaction is -5.3 Kcal/mol. The actual free-energy was calculated from standard state delta G' and known concentrations of reactants under typical physiological conditions. (5)