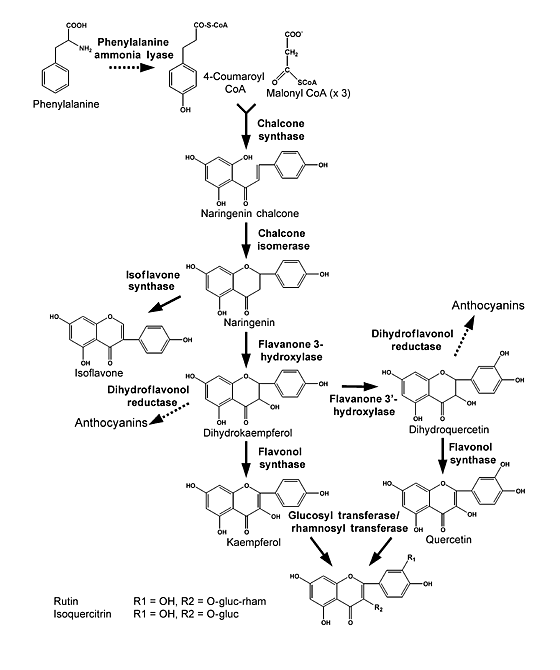
Chalcone isomerase is involved in the isoflavanoid pathway (Fig 1) (4). This pathway is responsible for the biosynthesis of flavonoid pigments and isoflavonoids. The pathway catalyzes the intramolecular cyclization of bicyclic chalcones into tricyclic flavanones. Also chaclone isomerase is involved in the biosynthesis of flavanone precursors of floral pigments and phenylpropanoid plant defense compounds. Plants use the flavanoids that the pathway produces for protection against UV light damage, attraction of pollinators to floral pigments, inducers of Rhizobium nodulation genes and for anti-microbial phytoalexins. The flavanoids produced can also exhibit medicinal properties, which can be common constituents in the human diet (5).
In contrast to the process of chalcone isomerase, mandelate racemase is involved in catalyzing the reversible interconversion of the (S)- and (R)- enantiomers of the mandelate anion (Figure 2) (4).
The third example, DNA topoisomerase 1, also gives a contrast to the other two pathways. DNA topoisomerase 1 is involved in DNA supercoil helix relaxation and introducing a temporary single-strand break in the DNA (Figure 3) (6). It also alters the topological state of DNA by passing one strand of the helix through the other strand (7). The enzyme is also involved in the elongation step and is associated with actively transcribed regions on chromatin and rRNA (8). These three enzymes are all involved in different pathways, but are still involved in the isomerization reaction that classifies them as isomerases.