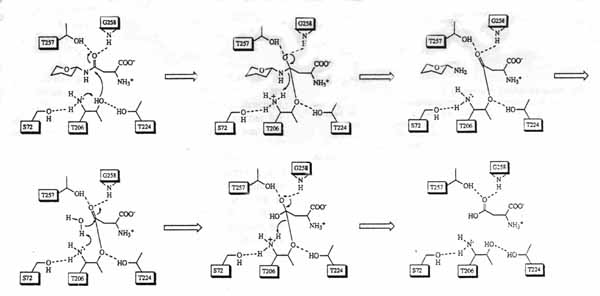
Mode of Action:
The mechanism through which aspartylglucosaminidase reacts is thought to be autocatalytic. The catalytic mechanism of AGA is like that of a Ser proteinase. The reaction catalyzed by AGA is one of the last steps in glycoprotein degradation. AGA breaks the amide bond between the asparagine and the oligosaccharide chain. The asparagine requires both a free alpha amino group and a free carboxy group for catalysis. The active site is buried deep within a funnel-shaped cleft that is formed by both subunits

Fig. 1
The picture above discribes the stated autocatalytic mechanism in organic terms. It was obtained from an EMBO J., article titled Functional analyses of active site residues of human lysosomal aspartylglucosaminidase: implications for catalytic mechanism and autocatalytic activation, written by Tikkanen, Riikonen, Oinonen, Rouvinen and Peltonen. (2)
Reaction Catalyzed by AGA: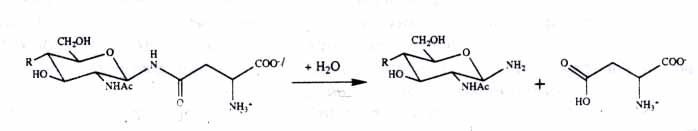
Fig.2
The reaction catalyzed by AGA. The amide linkage between the L-asparagine residue and glycan. Picture obtained from Nat. of struct. biology, article entitiled Three-dimensional structure of human lysosomal aspartylglucosaminidase.(6)