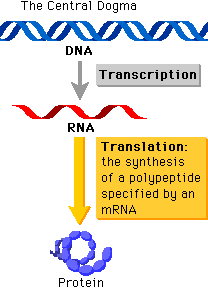
Transcription is the first and most essential part of gene expression. In figure 1, you see the central dogma of biology, DNA > RNA > Protein. Transcription is the process of converting the genes encoded in the DNA into RNA, which is the readable form for making proteins. Transcription involves the initiation, elongation, and termination of RNA synthesis. In eukaryotes, this is all done in the nucleus by the RNA Polymerase II along with a number of transcription factors. Genes that are transcribed are then said to be expressed because they are able to undergo translation. Further details about eukaryotic transcription plus the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic transcription will be covered in later pages.