1. Given the following reaction.
![]()
- Write the equilibrium constant expression, Ka, for this reaction. Recall that the ammonium ion (NH4+) is the conjugate acid for aqueous ammonia.
- Use the Virtual Lab Simulator, load the Unit 6 homework (File > Load Homework > Unit 6 > Elaborations - Definitions of Acids and Bases), and determine the pH of a 0.01 M solution of NH4Cl. Is NH4+ ion behaving like an acid as predicted by this equation?
(Note: Because NH4+ is ionic, to make up a 0.01 M solution of NH4+, you need to make up a solution of an ionic compound that contains NH4+. Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) is a good choice of an ionic compound for doing this.)
- Using the equilibrium concentrations that are determined by the Virtual Lab Simulator for the 0.01 M NH4Cl solution, calculate a value for Ka and pKa. Compare these values to the textbook values shown above in Figure 3.
-
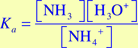 ,
,
The H2O is not included in this equation because it is the solvent and its concentration is unaffected by the reaction.
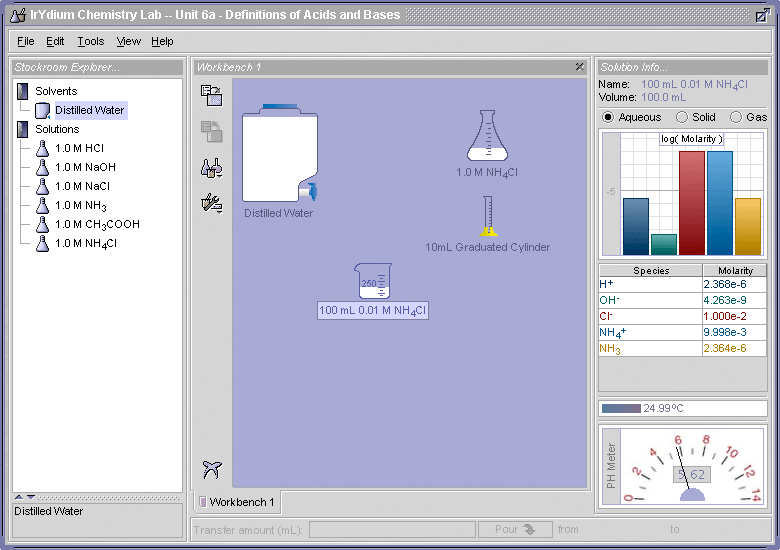
The pH is 5.62. Yes, the NH4+ ion is behaving like an acid because it lowered the pH of the solution from 7.0 to 5.62.
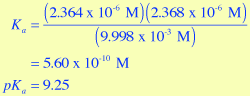 ;
;
These values agree quite well with those shown in Figure 3 for NH4+