Transcription and RNA Polymerase II
MIKE FREDERICKS
CHEM 406 Web Termpaper
FALL 2006
An Overview of the Transcription Process
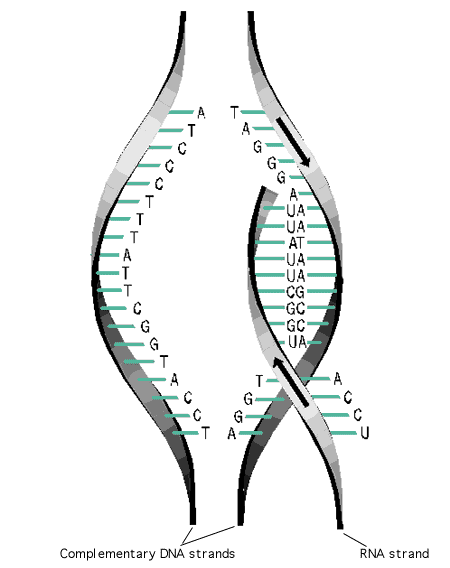
Introduction to the process of transcription.
Transcription is the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template. Whether occurring in prokaryotic or eukaryotic organisms, transcription has three main events: Initiation, Elongation and Termination. Although RNA Polymerase performs transcription, the enzyme needs assisting proteins to help initiate and produce the transcript. These factors either associate directly with RNA Polymerase or add in building the actual transcription complex apparatus to help regulate the appropriate transcript. The general term for such associated proteins are Transcription Factors. The process of transcription can be a rather overwhelming complex situation but if broken up into three main parts and separating know processes between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic organisms, a clear and concise view of the process can be reached.
Initiation –
Binding of the RNA polymerase and association of the initiation complex to promoter and enhancer regions on double-stranded DNA.
Elongation –
Covalent addition of ribonucleic bases to the 3` end of a growing chain pairing with a single stranded DNA template.
Termination –
Recognition of the transcription termination sequence and the release of RNA polymerase and the newly formed RNA polymer.
INSIGHT INTO THE PROCESS OF TRANSCRITPION
5 pages
COMPARING PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION
EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION– Detailed look at the process
DEADLY amanitin toxin from the Amanita phalloides mushroom
Contributions from Roger Kornberg's work in Eukaryotic Transcription leading to: